Heat gains calculations
Heat gains calculations
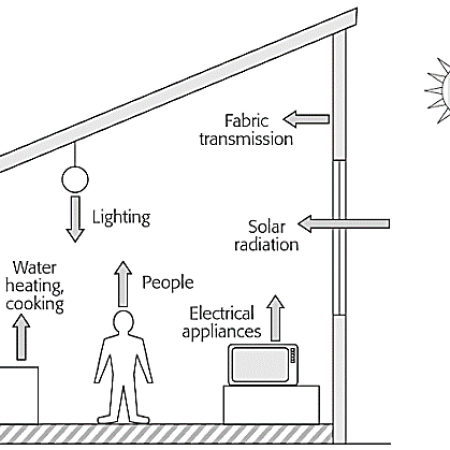
The total heat gains include heat gains from the sun, lighting, people, machines, devices, etc.
in which:
QW – gains from the sun via transparent barriers (windows) [W],
QWS – gains from the sun via non-transparent barriers (walls) [W],
QL – heat gains from lighting [W],
QP – heat gains from people [W],
QE – heat gains from electrical engines and machines [W],
QD – heat gains from other devices [W],
QIn – heat gains due to air infiltration [W],
QB – gains through barriers of adjacent rooms [W].
● Heat gains from people
Comprised of sensible and latent heat gains (i.e. humidity gains). Sensible heat gains can be calculated from the following formula
ø – people residence coincidence factor (from 0.4 to 1.0),
n – number of people,
qj – unitary heat flow delivered into the environment [W].
People residence coincidence factor depending on the room type
Note: In small buildings and in theatres, cinemas – ø = 1.
Sensible heat gains from people depending on the activity and temperature in the room [W].
● Latent heat gains (humidity gains)
wj – unitary flow of water steam delivered into the environment by a human depending on the activity and environment temperature [g/h].
Water steam gains depending on the activity and temperature in the room [g/h]
Note: For women, the values specified in table 2 and 3 must be decreased by 20%, while for children - by 20-40% depending on the age.
● Electrical lighting heat gains
Typical heat emissions from various sources of electrical light, calculated by simplified method shown in table.
● Heat gains from devices
It is necessary to assume on the basis of actual heat gains of devices installed in the room. If there is lack of such information, the gains can be adopted according to table. Approximate heat gains from devices.
● Heat gains from different electric devices
● Heat gains from the sun via transparent barriers (windows)
In typical conditions, many HVAC specialists use the simplified tables allowing for calculation of heat gains via transparent barriers. the gains can be adopted according to table.
However, in some cases, e.g. in rooms with large surfaces of transparent barriers and highly exposed to solar radiation, it is worth to conduct a detailed balance of the room’s heat gains.
● Heat gains from non-transparent barriers
Gains through the non-transparent barriers [W] by simplified method can be adopted according to the previous table.